Learning & Resources

Digital Learning with LinguaQuest App
Our Gamified App coming soon !
Script Characters
The Brahmi script is the oldest known Indian writing system, first appearing at least from the 3rd century BCE. Its Brahmi is an abugida, where the inherent vowel for each consonal phoneme is typically "a", and the other vowels are indicated by diacritical marks added to the consonant. The script is systematic and phonetic, with the characters organized by place and manner of articulation—similar to modern Indic scripts. The characters are usually geometric and simple, well-suited to be inscribed on metal and stone. From century to century, Brahmi developed into several regional scripts, which became the basis of scripts like Devanagari, Tamil, Kannada, Bengali, and many more.
Sharada script, which has originated in Kashmir in the 8th century CE, is a descendant of the Gupta script, which itself has evolved from Brahmi. Sharada letters are more complex and decorative than those of Brahmi, which indicates the transformation of scripts from stone inscriptions to writing on palm leaves and birch bark. It was primarily employed for Sanskrit and Kashmiri writing and is noted for its employment of religious and scholarly writings.
Brahmi Characters
Independent Vowels & Dependent Diacritics
- Independent vowel letters (like 𑀅 [a], 𑀇 [i], 𑀉 [u], 𑀎 [e], etc.) are used when a syllable begins with a vowel sound.
- Dependent vowel signs (diacritics) attach to consonants to override the inherent "a" and express other vowels.
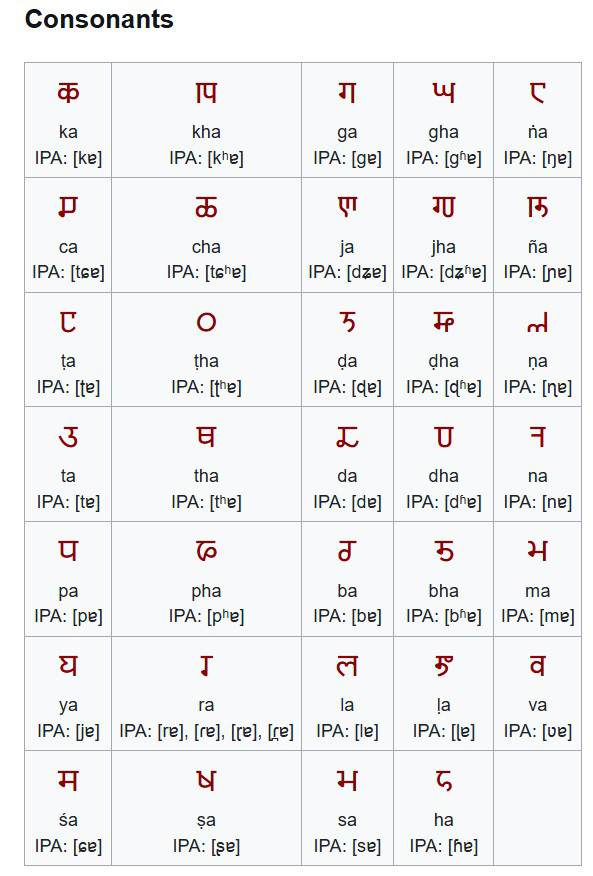
Consonants
- Gutturals : 𑀓 ka, 𑀔 kha, 𑀕 ga, 𑀖 gha, 𑀗 ṅa
- Palatals : 𑀘 ca, 𑀙 cha, 𑀚 ja, 𑀛 jha, 𑀜 ña
- Retroflexes : 𑀝 ṭa, 𑀞 ṭha, 𑀟 ḍa, 𑀠 ḍha, 𑀡 ṇa
- Dentals : 𑀢 ta, 𑀣 tha, 𑀤 da, 𑀥 dha, 𑀦 na
- Labials : 𑀧 pa, 𑀨 pha, 𑀩 ba, 𑀪 bha, 𑀫 ma
- Semi‑vowels & sibilants : 𑀬 ya, 𑀭 ra, 𑀳 la, 𑀯 va, 𑀰 śa, 𑀱 ṣa, 𑀲 sa, 𑀳 ha
- Gutturals : 𑀓 ka, 𑀔 kha, 𑀕 ga, 𑀖 gha, 𑀗 ṅa
- Gutturals : 𑀓 ka, 𑀔 kha, 𑀕 ga, 𑀖 gha, 𑀗 ṅa
Special Signs
- 𑁆 (Virama) : Suppresses the inherent vowel to form consonant clusters.
- 𑀺𑁆𑀭𑁆𑀬 (example) : kṛya = 𑀓𑀾𑁆𑀬

Sharda Characters
Vowels
Independent Vowels: 𑆃 a, 𑆄 ā, 𑆅 i, 𑆆 ī, 𑆇 u, 𑆈 ū, 𑆉 ṛ, 𑆊 ṝ, 𑆋 ḷ, 𑆌 ḹ, 𑆍 e, 𑆎 ai, 𑆏 o, 𑆐 au
Dependent Vowel Signs (Matras)
These are placed on consonants to replace the inherent "a":
- 𑆳 -ā, 𑆴 -i, 𑆵 -ī, 𑆶 -u, 𑆷 -ū, 𑆸 -ṛ, 𑆹 -ṝ, 𑆺 -ḷ, 𑆻 -ḹ, 𑆼 -e, 𑆽 -ai, 𑆾 -o, 𑆿 -au, plus signs for nasal ṃ (𑆀) and visarga ḥ (𑆂)
Consonants
Sharada features 34 consonant letters, each with an inherent "a" sound. The consonantal inventory breaks down as follows (isolated forms shown):
- Gutturals : 𑆑 ka, 𑆒 kha, 𑆓 ga, 𑆔 gha, 𑆕 ṅa
- Palatals : 𑆖 ca, 𑆗 cha, 𑆘 ja, 𑆙 jha, 𑆚 ña
- Retroflexes : 𑆛 ṭa, 𑆜 ṭha, 𑆝 ḍa, 𑆞 ḍha, 𑆟 ṇa
- Dentals : 𑆠 ta, 𑆡 tha, 𑆢 da, 𑆣 dha, 𑆤 na
- Labials : 𑆥 pa, 𑆦 pha, 𑆧 ba, 𑆨 bha, 𑆩 ma
- Semivowels & Sibilants : 𑆪 ya, 𑆫 ra, 𑆬 la, 𑆭 ḷa, 𑆮 va, 𑆯 śa, 𑆰 ṣa, 𑆱 sa, 𑆲 ha